
ZX-55100-96 | 8‐OHdG (DNA Damage) ELISA Kit
Free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are constantly generated in vivo during the normal metabolism, or due to ultraviolet and ionizing radiation. These endogenously- and exogenously- produced ROS can attack lipids, proteins and nucleic acids in living cells, and cause damage.
The process of oxidative damage in DNA results in the formation of 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), which is a regarded as a ubiquitous marker of oxidative stress. When individual bases are damaged, nonspecific DNA repair enzymes and base specific repair glycosylases excise DNA lesions and release deoxynucleotides, which are enzymatically hydrolyzed to stable deoxynucleosides. These repair products are transported through the blood and excreted in the urine. 8-OHdG is an oxidized derivative of deoxyguanosine that is formed during the repair of damaged DNA by exonucleases, and further excreted into urine. Damage to RNA is reflected in nucleoside adducts such as 8-Hydroxyguanosine (8-OHG).
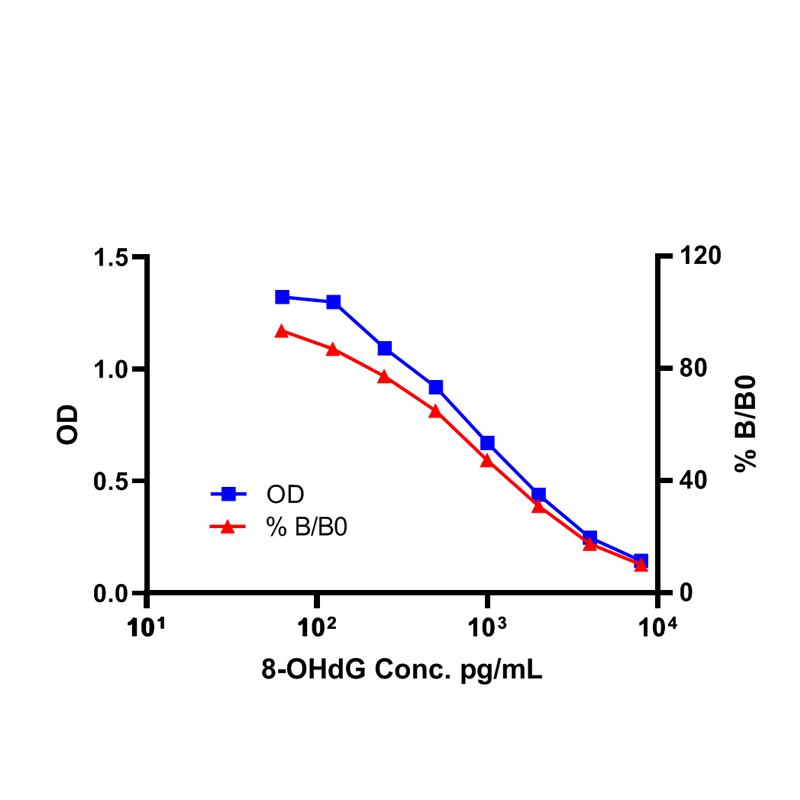
It is widely thought that continuous oxidative damage to DNA is a significant contributor to age-related development of the major cancers, such as those of the colon, breast, rectum, and prostate. 8-OHdG is physiologically formed and enhanced by chemical carcinogens. The ZellX® 8-OHdG ELISA Kit is designed to quantitatively measure oxidized guanosine species derived from damaged DNA and RNA molecules. The assay detects all three oxidized derivatives including 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), 8-hydroxyguanosine (8-OHG), and 8-hydroxyguanine which may be present in serum, plasma, saliva, urine, dried fecal samples, and tissue culture media samples.
Technical Support: Customer satisfaction is very important to us. Please call us at +49(0)30 81309085 or send an email to technical[at]zellx.de with your technical questions. A member of our scientific staff will be glad to assist you.